Purchase of companies
What is buyouts?
Buying a business is a process in which an investor, whether a company or an individual, acquires a business in which it has previously found interest due to the sector in which it is located, the opportunities it presents, its projection, etc.
In an increasingly dynamic competitive environment, inorganic growth strategies make it possible to gain competitive advantage more quickly and with less risk, although they require a financial investment in return. Buying going concerns can be a psychologically exhausting process for those without M&A experience. On the other hand, it requires dedication of time, effort and wear and tear.
Why buy a company? - Advantages of growing by acquiring
For the growth of a company, there are different strategic ways to grow apart from acquiring a company, such as innovation (internal development) or alliances with third party companies.
The advantages of growth by acquisition are:
- The acquiring company acquires control of the acquired company from the outset and therefore reduces risk.
- Acquiring companies generate a positive impact faster than innovation or alliances.
- M&A integrates new capabilities or strengths into the company.
On the other hand, acquiring companies has the following disadvantages:
- It requires a financial outlay or investment by the buyer.
- During the process, asymmetric information must be managed and therefore requires a careful process of analysis and evaluation and verification through due diligence.
- The integration of the acquired company is critical to the success of the transaction.
It may seem that only large corporations can acquire or merge with other companies, but it is a very valid open alternative for SMEs provided they have a clear growth strategy. The most important thing is to know how to do it to make it a success.
Good reasons to grow by acquiring
The most important thing - and this applies to any M&A transaction - is that an M&A transaction will make economic sense as long as it maximises shareholder value. Therefore, the basic objective of an acquisition is to generate synergies between the two companies that grow the value of the new combined company.
Depending on the type of transaction, the benefits vary:
- Horizontal integration: these are acquisitions in the same industry. Due to possible economies of scale, costs of production and purchasing or supply processes are reduced. Depending on the extent to which competition in the industry in which it operates is reduced, the company may be able to increase prices and thus increase its profit.
- Vertical integration: this is the acquisition of the customer or supplier. One of the objectives is to improve the technological alliance in order to integrate related activities. In addition, it allows the inputs and outputs that previously existed between the two companies to be controlled and, therefore, the purchasing and supply processes become internal processes with their consequent improvement in efficiency.
- Related diversification: acquisition or merger with companies in related industries. Similar assets are used and therefore costs may be shared.
- Unrelated diversification: acquisition or merger with companies in unrelated industries. No synergies are created, but available liquidity is used to diversify the conglomerate's balance sheet risk.
In addition to these operations, there are those of a more opportunistic type, where the value of the acquired business is expected to increase through an improvement in the management of the organisation or the sale of the various assets of the acquired company that are estimated to be undervalued.
Doubtful reasons to grow by acquisition
Among the reasons for an acquisition or merger, there are also some dubious ones, such as personal motivation of management, diversification of risk, effect on earnings per share, lower financing costs, growth for growth's sake, etc.
Key aspects for a successful process
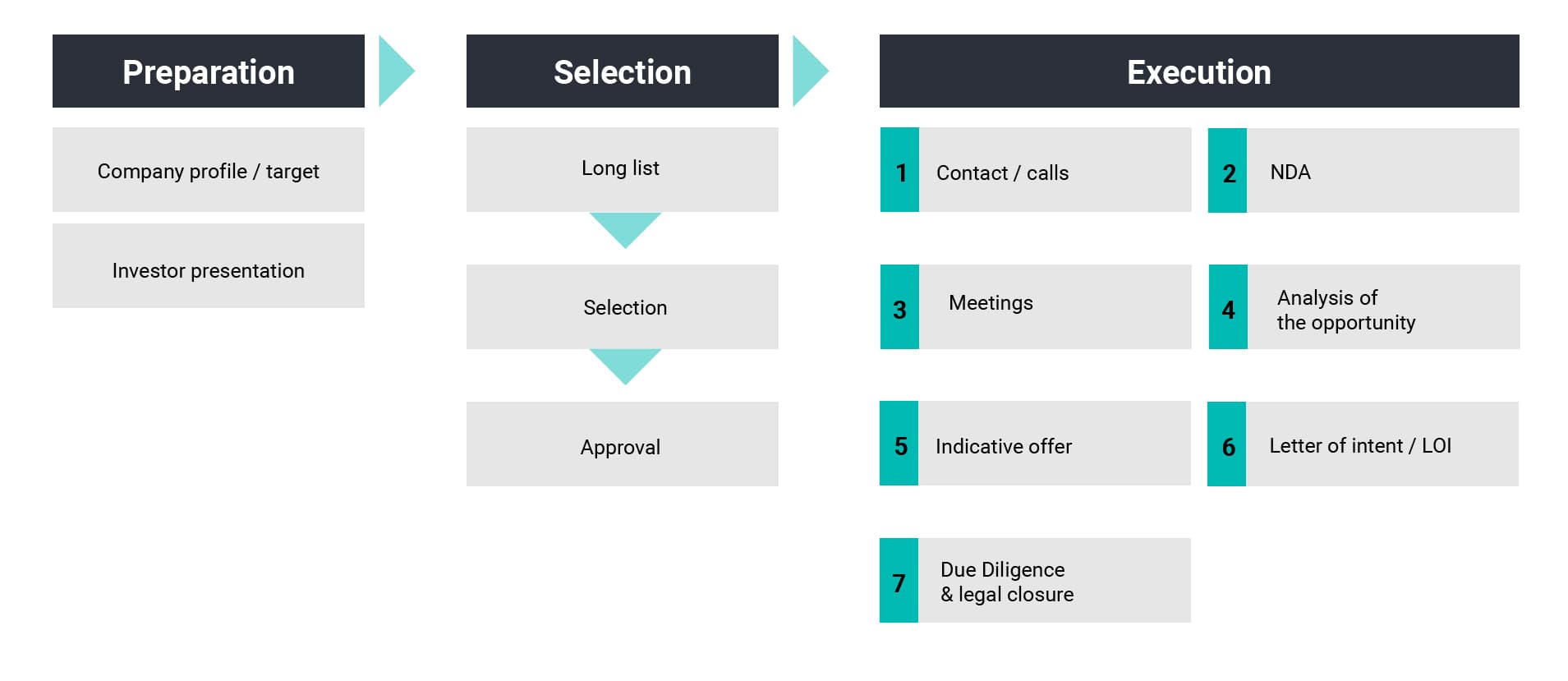
It is a process that requires in-depth research focused on the sectors in which the investor is interested; negotiation skills of an experienced professional to get a fair deal; knowledge of valuation, sale and purchase agreements and payments.
There are several aspects of the buying process that are key to determining its success:
- What - determination and valuation of synergy: before contacting any company, it is necessary to define the synergies sought, so as to know the value that the future incorporation may have.
- How - search, selection and integration plan: with clearly defined criteria, businesses can be searched for and selected objectively. The integration plan needs to be developed early to identify as soon as possible the problems that may lie in the details.
- Due Diligence: Apart from financial aspects, a thorough analysis of human capital is essential.
- Selection of the management team: determine the key team of the company to be acquired to drive growth.
- Integration of cultures: this aspect is not only relevant when acquiring foreign companies, but also in different organisations, as we can often find very different work cultures.
- Communication: Any change causes possible conflicts and doubts among employees, therefore, it is very important that once it has started, communication is continuous and clear. At the same time, it is good that the integration process is as agile as possible, without being uncontrolled.
Processes in the purchase of a business