Alternative finance
What is alternative financing and what are its advantages?
In Spain, more than 95% of companies are self-employed and SMEs, which have almost always resorted to traditional banks for their financing needs.
However, access to bank financing usually has its obstacles (guarantees, management costs, paperwork, lack of understanding of business models) that slow down or prevent them from obtaining the necessary financing for business development.
What is alternative financing?
Alternative financing, also called non-bank financing, is the set of financial markets and instruments that do not come from traditional banks. The sources of non-bank financing are diverse, but they all have in common the fact that there is no bank involved in the process. We are therefore dealing with "direct lending" - the owner of the money directly lends the capital, as he or she is the owner of the institution or fund making the loan.
As a general idea, alternative financing can be classified into equity investors (venture capital, business angels, etc.) and debt alternatives (debt funds, venture debt, etc.).
Advantages of alternative financing
Compared to bank financing
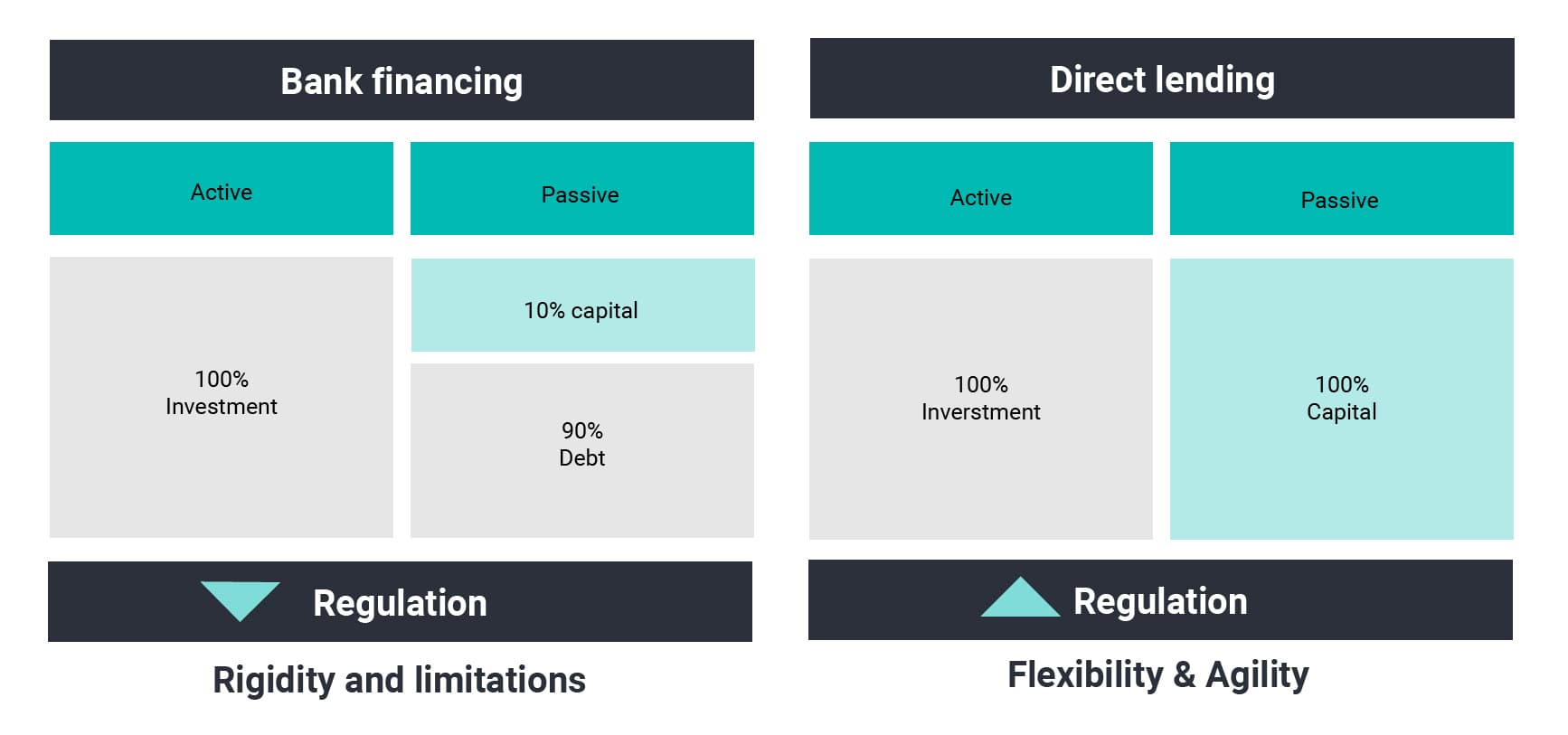
The main advantage of non-bank financing over traditional bank financing is the flexibility to adapt to the borrower's needs and cash flow generation.
Collateral is clearly less demanding for companies than in bank loans. The repayment period is longer and is generally in the form of a "bullet", i.e. 100% repayment at the end of the period. Since non-bank financing is less regulated, it can be obtained more quickly.
On the other hand, there are also disadvantages of alternative financing, such as the higher cost of financing, which usually includes a variable part. In most options, due diligence is required and the investor is required to obtain a seat on the board of directors, albeit without voting rights.
Versus Private Equity
Alternative financing does not involve the dilution of a company's existing shareholders, as would be the case when private equity becomes a shareholder. It also avoids the whole process of entry and exit of private equity and therefore does not require a joint negotiated exit after the investment process.
The negotiation process is simpler and more agile and the cost is lower compared to private equity. Equity is always the most expensive form of financing, as it assumes more risk. Finally, if venture capital enters the company, it will interfere in the management of the company.
What are the alternative sources of finance?
There is a fairly wide variety of sources in the market and the number of options available continues to grow. The suitability of each of the options depends on the company's purpose for financing.
Alternative financing for SMEs
Venture Debt
This is a financing alternative based on a combination of venture capital investment and a traditional loan. In exchange for receiving a loan of X amount, a combination of interest is paid and the company's capital is delivered. Due to its modality, it is a medium-term financing.
Cash Flow Lending
This is medium to long-term financing. The collateral for the loan is the expected cash flows that the company will generate. It is mainly used for the realisation of investments, purchase of assets, execution of projects and contracts.
Renting and Sale & Rentback on assets
This is the sale of a company asset, usually real estate, for subsequent long-term leasing. Long-term financing, basing the guarantee on the company's productive assets.
Company purchase financing loan
This is financing that is intended for the purchase of other companies or business units, customer portfolios or the like. The terms of the loan are determined by the solvency of the purchased party and the expected development of the business plan.
Bridge loan
This loan is intended for temporary and urgent financing needs, e.g. the need to cover cash flow in a timely manner. Sometimes they can also be used to obtain a larger definitive loan. Its main characteristic is its flexibility and agility.
Liquidity credit
It is dedicated to any cash flow need, whether it is punctual or recurrent. It can be, for example, to finance purchases or to diversify and complement the sources of financing of working capital.
Non-recourse factoring
In so-called non-recourse factoring, the company assigns the right to collect and the risk of its invoices in exchange for receiving the amount before the due date of the invoices. This financing improves solvency, debt and liquidity ratios. This financing does not appear on the company's balance sheet.
Alternative financing for large investments
Alternative financing is mostly spoken of only in the context of start-ups and small investments. On the contrary, however, it is also available for larger projects. In this context, compared to a bank loan or a venture capital investment, it has the great advantage that it does not count towards CIRBE, given its non-bank status.
- Direct lendingis a direct way of providing financing to the company in which the lender is other than a financial or banking entity. The actors are investment funds, which grant loans to companies with the aim of obtaining a return on their investors' capital.
- Borrowers are usually small or medium-sized enterprises(SMEs) rather than large listed companies or large corporations that already have access to corporate bond issuance, for example.
- Lenders can be high net worth individuals or families or asset management companies. However, they will only consider loans above €5m, typically. Therefore, direct lending is mainly focused on middle-market borrowers.
Many entrepreneurs and managers are hesitant to achieve and implement their fundraising objectives and raise funds in line with the defined strategy:
- Financing strategy: When is it appropriate to use alternative financing and what is the optimal risk/return point?
- Identification and evaluation of options: What sources of finance are available and which is the most suitable for me given my company's situation?
- Executing the deal: How do I get the best terms? How do I make my investment proposal more attractive to attract the best fund?
- Closing: How do I manage communications with the deal's stakeholders?
- Ongoing communication with management and stakeholders: How do I manage communications with stakeholders to maintain shareholder support?